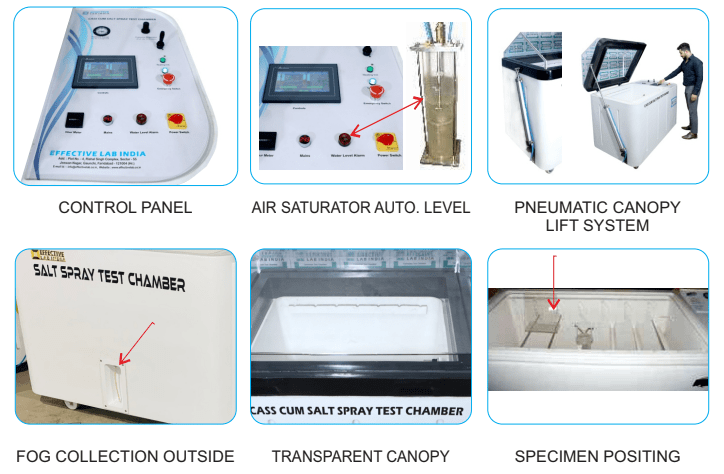
Have you ever wondered how manufacturers ensure that their products can withstand challenging environmental conditions? Explore the salt spray test chamber, specialized equipment intended to evaluate a material’s ability to withstand corrosion. This chamber is essential when evaluating whether a product can survive in an area where rust and degradation are common.
In this blog, we’ll explain in great detail what a salt spray test chamber is, how it functions, and why it is important in testing materials in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, coating and plating, and marine sectors.
What is a Salt Spray Test Chamber?
A salt spray test machine is lab equipment that exposes materials to salt mist or fog to simulate corrosive conditions. To help businesses predict real-world performance, it is widely used to demonstrate how the coating, material, or coating resists corrosion better over time.
How Does a Salt Spray Test Chamber Work?
Salt spray chambers replicate the natural environment where metals and other materials are prone to rust or corrosion. Here’s a closer look at how the process works:
Spraying Process Explained
To create the effect of fog, a solution of water and sodium chloride (salt) is sprayed into the chamber. This saline mist is continuously applied to the material object that is being tested, simulating the conditions that lead to corrosion under external conditions.
Controlled Environment for Testing
The chamber maintains controlled temperature and humidity levels to ensure consistency throughout the test. Factors like pH value and spray pressure are closely monitored to meet specific testing standards, such as ASTM B117.
Components of a Salt Spray Test Chamber
Understanding the key components helps you appreciate how efficiently these chambers work:
- Test Chamber Body: The enclosure where the test samples are placed.
- Salt Solution Reservoir: Stores the salt-water mixture used for the spray.
- Air Supply System: Provides compressed air to atomize the salt solution into mist.
Types of Salt Spray Test Chambers
There are two main types of salt spray chambers:
Continuous Salt Spray Test Chambers
These chambers continuously exposed samples to a salt mist, simulating conditions found in marine or coastal regions.
Cyclic Corrosion Test Chambers
The cycle chambers alternate between salt spray, dry, and humidity cycles to simulate more complex environmental conditions.
The Purpose of Salt Spray Testing
Evaluating corrosion resistance is the main objective of salt spray testing. This test offers vital information on how coatings and materials will function in challenging circumstances.
Industries Using Salt Spray Chambers
Several industries rely on salt spray testing to validate their products:
Automotive Industry
It is used by car manufacturers to ensure the durability of metal parts and to prevent premature wear on exposed surfaces.
Aerospace Sector
Aircraft parts are tested to ensure they can withstand corrosion at altitude and in various weather conditions.
Electronics Industry
Sensitive electrical devices are tested to determine their resistance to corrosion in a wet or marine environment.
Marine Applications
Ship components undergo salt spray testing to ensure longevity in salty, corrosive waters.
Benefits of Salt Spray Testing
- Accurate Predictions: Assists in estimating the life of coatings and materials.
- Quality Control: Guarantees that finished products fulfill industry requirements.
- Cost-effective: By mimicking everyday life conditions in a controlled atmosphere, it eliminates the need for field testing.
Limitations of Salt Spray Test Chambers
These chambers are useful, but they are not without restrictions. It’s possible that they can’t accurately simulate intricate corrosion environments, such as ones with UV exposure or temperature swings.
The Importance of Salt Spray Testing in Material Quality Assurance
For businesses to achieve quality standards and guarantee that their products are functional, salt spray testing is essential. Additionally, it lowers the possibility of field failures by assisting manufacturers in locating weak areas in materials and coatings.
Latest Market Trends in Salt Spray Testing
- Eco-Friendly Testing Methods: Many companies are adopting sustainable practices by using low-toxicity salt solutions.
- Automation and IoT Integration: Modern chambers offer remote monitoring and automated testing features.
- Demand for Customized Testing: Different industries require specialized test conditions, leading to the development of custom salt spray chambers.
Best Practices for Using Salt Spray Chambers
- Follow Test Standards: To guarantee consistent outcomes, abide by standards such as ASTM B117.
- Calibrate Regularly: It is important to calibrate regularly to guarantee precise spray and temperature levels.
- Use Quality Salt Solutions: Steer clear of contaminants in the salt solution as they may influence test results.
Maintenance Tips for Salt Spray Test Chambers
- Clean the Nozzles: Keeping spray nozzles clean helps to avoid salt accumulation.
- Check Seals and Gaskets: Examine gaskets and seals to make sure the chamber is airtight and able to hold the right humidity levels.
- Inspect Air Filters: Examine the air filters and replace any blocked ones to keep the spray pressure steady.
Future of Salt Spray Test Chambers in the Market
With the development of automated and AI-powered chambers which produce more accurate results, the future appears bright. Green testing procedures are also gaining a lot of attention as businesses seek to reduce their environmental effect.
To know the best price of a salt spray chamber Visit: https://saltspraychamber.com/salt-spray-test-chamber
Conclusion
Salt spray test chambers are essential for assisting companies in determining how resistant their products are to corrosion. This testing process guarantees that materials function as intended in challenging environmental circumstances, which is important for industries like the automotive and marine sectors. In the near future, we may anticipate even more creative, effective, and environmentally friendly testing options as advances in technology occur.