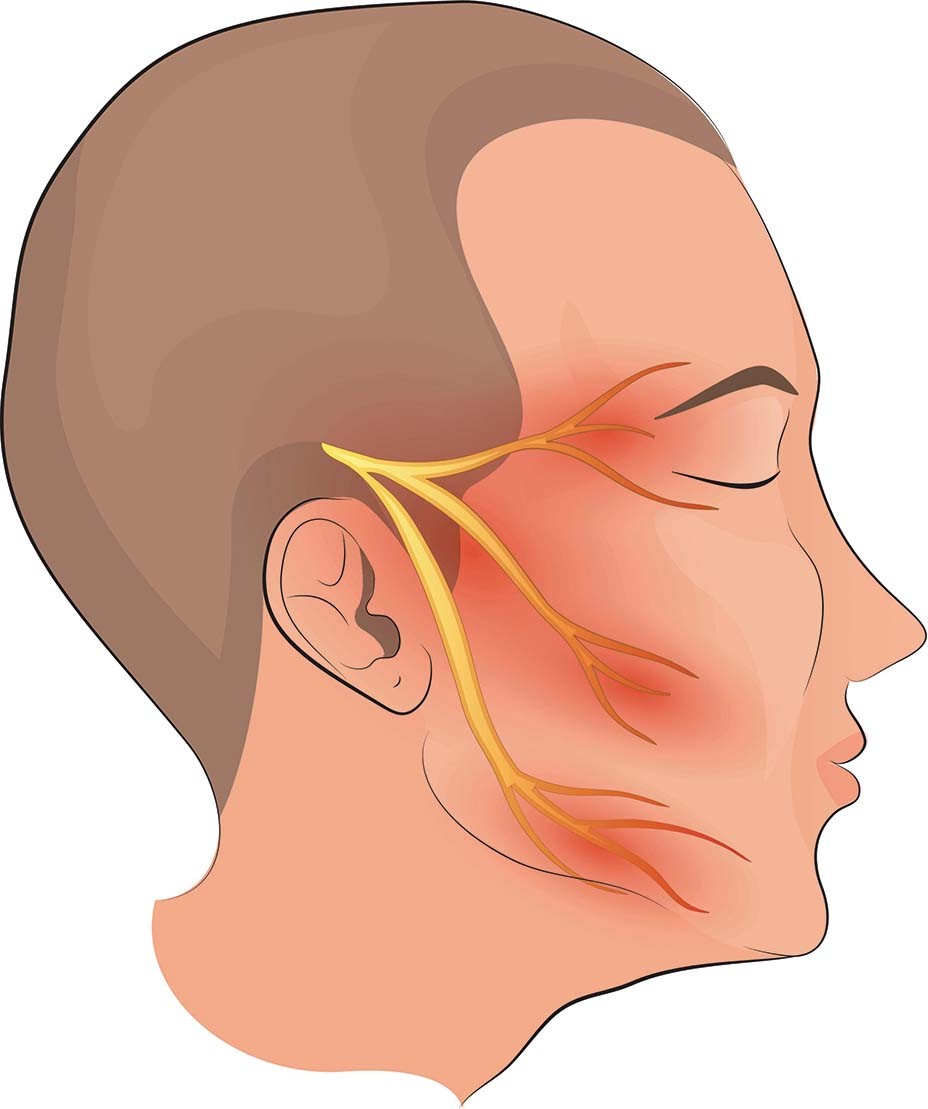
Face-piercing, excruciating pain is a symptom of the neurological condition trigeminal neuralgia. This illness affects the trigeminal nerve, which sends feelings from the face to the brain. Pain from trigeminal neuralgia may be severe and have a substantial influence on quality of life. In this post, we’ll look at trigeminal neuralgia, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment choices.
What Are the Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia?
The specific aetiology of trigeminal neuralgia is often unknown. However, it is believed to be the result of trigeminal nerve irritation or compression. Several variables may contribute to compression, such as:
Blood Vessel Compression: In certain circumstances, adjacent blood vessels might compress the trigeminal nerve, causing the distinctive pain of trigeminal neuralgia.
Trigeminal neuralgia may also develop in those who have multiple sclerosis, a disorder that affects the central nervous system.
Nerve Damage: Injury or surgery to the trigeminal nerve may also cause trigeminal neuralgia.
Prosoma 500mg is mostly formed of the active component carisoprodol. Carisoprodol is a muscle relaxant used to relieve muscular spasms and pain. It works by altering neuronal transmission in the central nervous system, which helps to relieve muscular discomfort and tension.
Symptoms Of Trigeminal Neuralgia
The most common symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is sudden, intense face discomfort. This pain is often characterised as intense, shooting, or electric shock-like, and it usually only affects one side of the face. Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia include:
Episodic Pain: Trigeminal neuralgia pain is characterised by abrupt, unexpected bouts that may last anywhere from seconds to minutes.
Trigger Factors: Certain actions or triggers, such as touching the face, eating, talking, or simply feeling a wind, may cause or increase discomfort.
Pain Distribution: Pain is usually limited to certain parts of the face, such as the cheek, jaw, or forehead, which correlate to the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Diagnosizing Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is diagnosed after a thorough examination of the patient’s symptoms and history. Your healthcare practitioner may also do a physical examination and prescribe other tests, such as:
A comprehensive neurological examination may help determine facial feeling, muscular strength, and reflexes.
Imaging studies: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be required to rule out any other underlying reasons, including as tumours or multiple sclerosis.
Diagnostic Nerve Blocks: Nerve blocks, which include injecting a local anaesthetic near the trigeminal nerve, may help confirm a diagnosis by momentarily alleviating pain.
Prosoma 350mg is generally used as a muscle relaxant. Its primary element is carisoprodol, which acts by inhibiting pain signals between neurons and the brain. It is often recommended for the temporary alleviation of acute musculoskeletal pain or discomfort. Prosoma 350mg should be taken with caution and under the supervision of a healthcare expert, since it has habit-forming properties and may produce drowsiness or dizziness.
Treatment Alternatives for Trigeminal Neuralgia
Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia attempts to reduce pain and enhance quality of life. Treatment options may include:
Anticonvulsant drugs, such as carbamazepine or gabapentin, are often recommended to alleviate nerve pain caused by trigeminal neuralgia.
Surgical Interventions: When drugs are unsuccessful or poorly tolerated, surgical treatments may be suggested. Microvascular decompression, gamma knife radiosurgery, and percutaneous techniques like radiofrequency ablation or balloon compression are all viable options.
Alternative treatments: Some people may benefit from complementary and alternative treatments including acupuncture, biofeedback, or relaxation methods.
Is trigeminal neuralgia a serious condition?
Trigeminal neuralgia, which produces intense, excruciating pain, may have a substantial effect on quality of life. While the illness is rarely life-threatening, persistent pain may cause mental suffering, despair, and difficulties doing everyday tasks. Early detection and effective treatment are critical for controlling symptoms and improving overall health.
In conclusion, trigeminal neuralgia is a neurological disorder characterised by severe face discomfort. Although the exact cause is unknown, there are effective therapeutic options available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those who suffer from this disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Trigeminal Neuralgia
Q: What is trigeminal neuralgia?
A: Trigeminal neuralgia is a neurological disorder characterized by intense, stabbing pain in the face. It affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for transmitting sensations from the face to the brain.
Q: What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
A: The exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia is often unknown. However, it is believed to result from compression or irritation of the trigeminal nerve by nearby blood vessels, multiple sclerosis, or nerve damage.
Q: What are the symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia?
A: Common symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia include sudden, severe facial pain that is described as sharp, shooting, or electric shock-like. The pain typically affects one side of the face and may be triggered by activities such as touching the face, chewing, or talking.
Q: How is trigeminal neuralgia diagnosed?
A: Diagnosing trigeminal neuralgia involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Additional tests such as MRI or CT scans may be ordered to rule out other underlying causes, and diagnostic nerve blocks may be performed.
Q: What are the treatment options for trigeminal neuralgia?
A: Treatment for trigeminal neuralgia aims to alleviate pain and improve quality of life. Options may include medications such as anticonvulsants, surgical interventions like microvascular decompression or gamma knife radiosurgery, and alternative therapies such as acupuncture or relaxation techniques.
Q: Is trigeminal neuralgia a serious condition?
A: While trigeminal neuralgia itself is not life-threatening, the chronic nature of the pain can significantly impact quality of life and lead to emotional distress and difficulty performing daily activities. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.